Ensures vaccine efficacy.
Critical for maintaining public health.
Prevents spoilage and wastage.
Optimal Temperature Range: Vaccine refrigerators must consistently maintain temperatures between 2°C and 8°C to ensure the efficacy of vaccines.
Digital Thermometers: Accurate digital readouts for constant monitoring.
Data Loggers: Record temperature data over time for compliance and audits.
Thermocouples: Measure and control temperature with high precision.
Regular Calibration: Ensures that temperature readings remain accurate.
Professional Services: Utilize certified technicians for calibration.
Traceable Standards: Adhere to national and international calibration standards.



High-Quality Insulation Materials: Maintain internal temperature despite external conditions.
Sealed Doors: Prevent warm air infiltration.
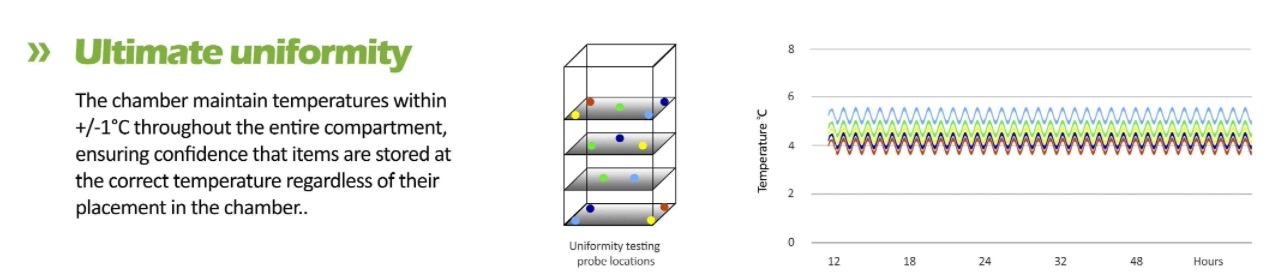
Temperature Uniformity: Ensures consistent temperature throughout the unit.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): Provide temporary power during outages.
Generators: Long-term backup power solutions.
Battery Packs: Portable backup for mobile units.
Temperature Excursion Alarms: Immediate alerts for any deviations from the set range.
Remote Monitoring: SMS or email notifications for off-site monitoring.
Visual and Audible Alerts: On-site alarms for quick response.
Thermal Mapping Studies: Identify cold and hot spots within the unit.
Regular Assessments: Conduct periodic mapping to ensure uniform temperature distribution.
Adjustable Shelving: Optimize airflow and temperature stability.
Ambient Temperature Control: Maintain stable room temperature to support refrigerator performance.
Humidity Control: Manage humidity levels to enhance refrigeration efficiency.
Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation around the unit to prevent overheating.
Routine Checks: Regular inspections to identify and rectify issues promptly.
Cleaning: Keep condenser coils and internal components clean to maintain efficiency.
Preventive Maintenance: Scheduled servicing to prevent breakdowns and ensure longevity.
Adherence to Guidelines: Follow specific instructions for installation and operation.
Regular Updates: Stay informed about any updates or modifications from the manufacturer.
Compliance with Standards: Ensure the refrigerator meets relevant health and safety standards.
Proper Usage Training: Educate users on correct operation and handling.
Emergency Protocols: Train staff on procedures for power outages and equipment failures.
Ongoing Education: Continuous training sessions to keep staff updated on best practices.
Live attenuated vaccines require stable temperatures.
Inactivated vaccines are less sensitive but still need cold storage.
Specific guidelines for each vaccine type.
Loss of potency and effectiveness.
Increased risk of disease outbreaks.
Financial loss due to wasted vaccines.
Ideal for small clinics.
Occupy minimal space.
Easy to transport.
Suitable for hospitals and large health centers.
High storage capacity.
Robust and durable.
Essential for outreach programs.
Lightweight and mobile.
Battery or solar-powered options.
Accurate temperature control from 2°C to 8°C.
Essential for vaccine stability.
Regular calibration ensures accuracy.
Reduces operational costs.
Environmentally friendly refrigerants.
Solar-powered options for off-grid areas.
Continuous temperature monitoring.
Alarm systems for temperature deviations.
Data logging for compliance and audits.
Alerts for temperature excursions.
Lockable doors for security.
Backup power systems.
Adjustable shelving for different vial sizes.
Configurable layouts for optimal space utilization.
Suitable for varying volumes of vaccine stock.
High ambient temperatures.
Humidity affects refrigeration efficiency.
Need for robust, reliable systems.
Centralized distribution centers.
Transportation to remote areas.
Cold chain logistics management.
Urban centers have better infrastructure.
Rural areas face accessibility issues.
Mobile solutions for remote locations.
Evaluate current and future vaccine volumes.
Consider the types of vaccines stored.
Space and capacity requirements.
Compare features and specifications.
Check reviews and testimonials.
Look for reputable manufacturers.
Initial purchase cost vs. long-term savings.
Energy consumption and maintenance costs.
Budgeting for essential features.
Ensure comprehensive warranty coverage.
Access to reliable customer support.
Availability of spare parts and service.
Follow manufacturer guidelines.
Ensure proper ventilation and spacing.
Electrical safety considerations.
Scheduled cleaning and servicing.
Regular calibration checks.
Preventive maintenance routines.
Identifying temperature inconsistencies.
Addressing power failures.
Repairing malfunctioning components.
Engage certified technicians.
Regular servicing contracts.
Emergency repair services.
Enhanced vaccine storage in urban hospitals.
Improved immunization rates.
Case studies from leading hospitals.
Overcoming logistical challenges.
Innovative storage solutions.
Success stories from rural clinics.
Backup power solutions.
Solar-powered refrigerators.
Ensuring uninterrupted storage.
Proper shelving and arrangement.
Use of temperature mapping.
Regular monitoring and adjustments.
Mobile refrigeration units.
Efficient cold chain logistics.
Collaboration with local communities.
Comprehensive training modules.
Hands-on workshops.
Ongoing education and support.
24/7 technical helplines.
On-site support services.
Online resources and FAQs.
Government guidelines and protocols.
Manufacturer manuals and guides.
Industry publications and research.